- Home
- Brain Tumor
Brain Tumor
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells in or around the brain. While hearing the term “brain tumor” can be alarming, not all tumors are cancerous.
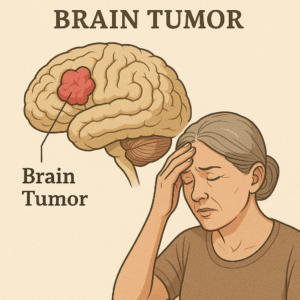
What Is a Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor occurs when cells in the brain grow uncontrollably, forming a mass. Tumors can be:
Benign (Non-Cancerous): These tumors grow slowly and don’t spread to other parts of the body.
Malignant (Cancerous): These are aggressive and can spread to other areas of the brain or body.
Types of Brain Tumors
Primary Brain Tumors: Originate in the brain. Examples include:
- Gliomas: Affect the brain’s supportive tissue.
- Meningiomas: Arise from the meninges, the brain’s protective layers.
- Pituitary Tumors: Develop in the pituitary gland, affecting hormone regulation.
- Medulloblastomas: Common in children, affecting the brainstem.
Secondary (Metastatic) Brain Tumors: Spread from cancers in other parts of the body, such as the lungs, breasts, or skin.
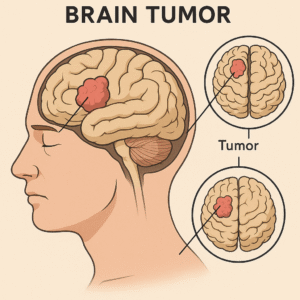
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of brain tumors remain unclear, but several factors may increase the risk, including:
Genetic Mutations
Changes in DNA that affect cell growth.
Family History
A family history of brain tumors or genetic conditions.
Radiation Exposure
Previous radiation therapy or environmental exposure.
Age
Some types are more common in children, while others occur more frequently in adults.
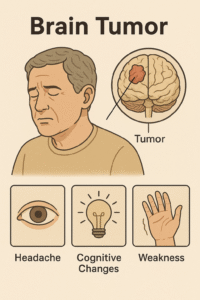
Common Symptoms of Brain Tumors
Symptoms depend on the tumor’s size, location, and rate of growth. Common signs include:
- Persistent headaches, especially in the morning
- Nausea and vomiting
- Seizures
- Memory problems or confusion
- Vision, speech, or hearing difficulties
- Weakness or numbness in limbs
- Personality or mood changes
Seek medical attention if these symptoms persist or worsen over time.


Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
Doctors use a range of tests to diagnose brain tumors, including:
Neurological Exams
Assessing vision, coordination, reflexes, and more.
Imaging Tests
MRI and CT scans to locate the tumor.
Biopsy
A sample of tumor tissue for detailed examination.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the tumor’s type, size, and location, as well as the patient’s overall health. Common treatments include:
1. Surgery: Removing the tumor when possible.
2. Radiation Therapy: Using high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
3. Chemotherapy: Medications to kill or slow tumor growth.
4. Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific genetic changes in cancer cells.
5. Immunotherapy: Boosting the immune system to fight the tumor.
Rehabilitation services like physical therapy, speech therapy, and counselling may also be needed after treatment.
While a brain tumor diagnosis can be daunting, advances in medical technology and treatment options offer hope. Early detection and timely intervention are crucial for better outcomes. If you or a loved one experiences concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly.

